File Management#
Files, Images and Folders as database records#
All files, images and folders in the 'assets' directory are stored in the database. Each record has the following database fields:
| Field name | Description |
|---|---|
ClassName | The class name of the file (e.g. File, Image or Folder). |
Name | The 'basename' of the file, or the folder name. For example 'my-image.jpg', or 'images' for a folder. |
Title | The optional, human-readable title of the file for display only (doesn't apply to folders). |
Filename | The path to the file/folder, relative to the webroot. For example 'assets/images/my-image.jpg', or 'assets/images/' for a folder. |
Content | Typically unused, but handy for a textual representation of files. For example for fulltext indexing of PDF documents. |
ShowInSearch | Whether the file should be shown in search results, defaults to '1'. See "Tutorial 4 - Site Search" for enabling search. |
ParentID | The ID of the parent Folder that this File/Folder is in. A ParentID of '0' indicates that the File/Folder is in the 'assets' directory. |
OwnerID | The ID of the Member that 'owns' the File/Folder (not related to filesystem permissions). |
Management through the "Files" section of the CMS#
If you have the CMS module installed, you can manage files, folders and images in the "Files" section of the CMS. Inside this section, you will see a list of files and folders like below:
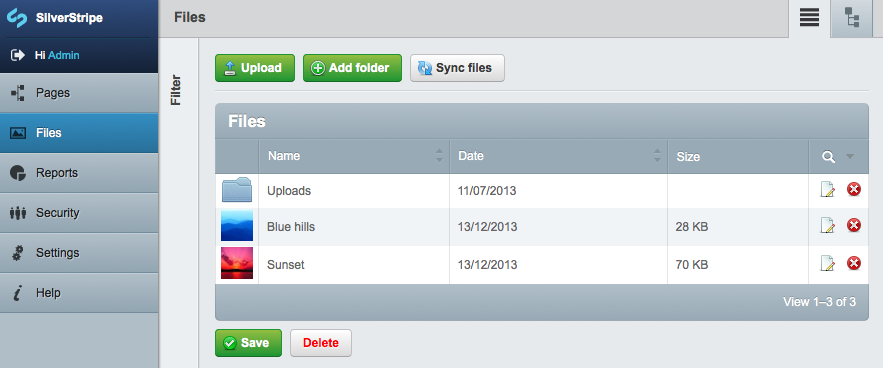
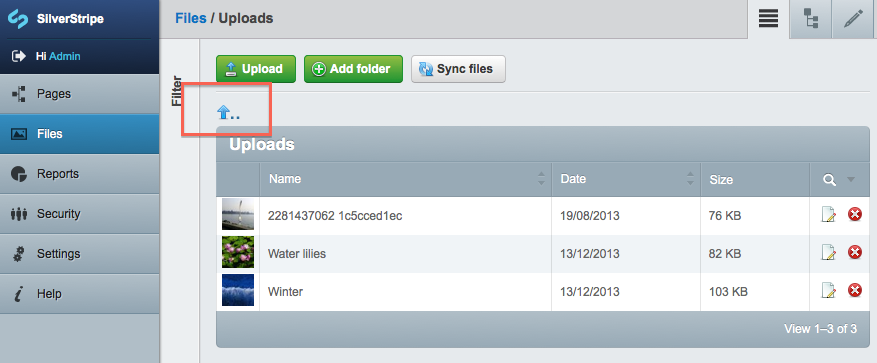
You can click on any file to edit it, or click on any folder to open it. To delete a file or a folder, simply click the red 'X' symbol next to it. If you click to open a folder, you can go back up one level by clicking the 'up' arrow above the folder name (highlighted below):
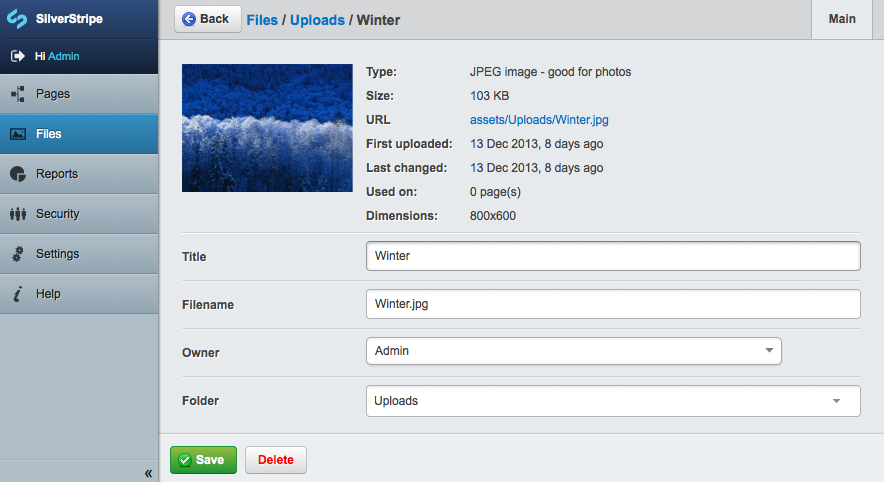
Once you click to edit a file, you will see a form similar to the one below, in which you can edit the file's title, filename, owner, or even change which folder the file is located in:
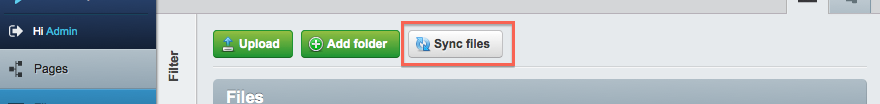
You may also notice the 'Sync files' button (highlighted below). This button allows CMS users to 'synchronise' the database (remember, all files/folders are stored as database records) with the filesystem. This is particularly useful if someone has uploaded or removed files/folders via FTP, for example.
Upload#
Files can be managed through a FileField or an UploadField. The FileField class provides a simple HTML input with a type of "file", whereas an UploadField provides a much more feature-rich field (including AJAX-based uploads, previews, relationship management and file data management). See Reference - UploadField for more information about how to use the UploadField class.